Make a donation
Baguio topographic map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Make a donation
Baguio
In 1903, Filipinos, Japanese and Chinese workers were hired to build Kennon Road, the first road directly connecting Baguio with the lowlands of La Union and Pangasinan. Before this, the only road to Benguet was Naguilian Road, and it was largely a horse trail at higher elevations. Camp John Hay was established on October 25, 1903 after President Theodore Roosevelt signed an executive order setting aside land in Benguet for a military reservation for the United States Army. It was named after Roosevelt's Secretary of State, John Milton Hay.
Make a donation
About this map
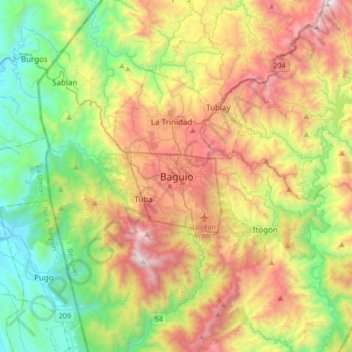
Name: Baguio topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Baguio, Cordillera Administrative Region, 2600, Philippines (16.25200 120.43337 16.57200 120.75337)
Average elevation: 881 m
Minimum elevation: 24 m
Maximum elevation: 2,226 m
Make a donation
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Metro Manila
The Coastal Margin or Lowland is a flat and low plain that faces Manila Bay. Located here is Manila, Navotas, parts of Malabon, and the western part and reclaimed areas of Pasay and Parañaque, where the ground elevation ranges from zero meters on Manila Bay to five meters at the west side of the cities of…
Average elevation: 43 m
San Jose del Monte
The elevation of the city ranges from approximately 40 to 900 meters (130 to 2,950 ft) above sea level; the relief transitions from warm lowland to cool upland as one goes eastward. This is because the city is part of the Sierra Madre mountain range. Plains and river valley flats characterize the western and…
Average elevation: 73 m
Make a donation
Baguio
In 1903, Filipinos, Japanese and Chinese workers were hired to build Kennon Road, the first road directly connecting Baguio with the lowlands of La Union and Pangasinan. Before this, the only road to Benguet was Naguilian Road, and it was largely a horse trail at higher elevations. Camp John Hay was…
Average elevation: 1,371 m
Make a donation
Isabela
The province is divided into three physiographic areas. The eastern area, straddled by the Sierra Madre mountain range, is rugged and thickly forested. A substantial portion is uncharted. These unexplored hinterlands are home to a rich variety of flora and fauna, and some are under government reservations. It…
Average elevation: 227 m
Lipa
At the celebration of the elevation of Lipa to a city in January 1888, José Rizal was invited by Dr. Jose Lozada, Catalino Dimayuga and the brothers Celestino and Simeon Luz but Rizal responded only with his Hymno Al Trabajo which he dedicated to the zeal and industry of the Lipeños.
Average elevation: 208 m
Quezon City
In order to make Quezon's dream a reality and to mobilize funds for the land purchase, the People's Homesite Corporation (PHC) was created on October 14, 1938, as a subsidiary of NDC, with an initial capital of ₱2 million. Roces was the chairman of the Board of PHC, and they immediately acquired the vast…
Average elevation: 39 m
Make a donation
Muntinlupa
There are three plausible origins of the name of the city: First, is its association with the thin topsoil in the area; second, residents, purportedly replying to a question by Spaniards in the 16th century what the name of their place was, said “Monte sa Lupa”—apparently mistaking the question for what…
Average elevation: 21 m
Wangal, La Trinidad, Benguet
Philippines > Benguet > La Trinidad > Wangal > Ampasit
Average elevation: 1,352 m
Make a donation
Make a donation
Cavite
Another theory proposes that the name is a Hispanicized form of kabit, Tagalog for "joined", "connected", or "attached", referring to the peninsula's topographical relation to the mainland. Edmund Roberts, in his 1821 memoir, stated that the "natives" called it Caveit due to the "crooked point of land…
Average elevation: 88 m
Cagayan de Oro
Cagayan de Oro, located along the north-central coast of Mindanao, Philippines, encompasses a diverse topography that significantly influences its terrain. The city spans approximately 488.86 square kilometers (188.75 square miles), featuring a 25-kilometer (16 miles) coastline along Macajalar Bay. The…
Average elevation: 224 m
Make a donation
Taytay
The shape of Taytay is rectangular – trapezoidal with gently hilly rolling terrain on its eastern side while relatively flat on its south-western side, including the poblacion. The municipality's highest elevation ranges from 200 to 255 meters which is situated along the inner north-eastern hills of Barangay…
Average elevation: 37 m
Make a donation
Dasmariñas
Dasmariñas is partly lowland and partly hilly. The Poblacion itself is elevated. From an elevation of 80 meters (260 ft) at the Poblacion, the land rises to 250 meters (820 ft) towards Silang. Generally, land near rivers and creeks are rugged. Dasmariñas is outside the typhoon belt and has no fault line…
Average elevation: 126 m
Tagaytay
It is one of the country's most popular destinations for domestic tourism because of its scenery and cooler climate provided by its altitude. Tagaytay overlooks Taal Lake in Batangas and provides views of Taal Volcano Island in the middle of the lake through various vantage points situated in the city.
Average elevation: 348 m
Make a donation
Cagayan de Oro
Cagayan de Oro, located along the north-central coast of Mindanao, Philippines, encompasses a diverse topography that significantly influences its terrain. The city spans approximately 488.86 square kilometers (188.75 square miles), featuring a 25-kilometer (16 miles) coastline along Macajalar Bay. The…
Average elevation: 224 m
Bataan
Bataan is divided by two mountain groups of volcanic origins. The northern side is composed of the Mount Natib (elevation 1,253 metres (4,111 ft)), Mount Sta. Rosa and Mount Silangan. The southern group is composed of Mount Mariveles, Mount Samat, and Mount Cuyapo. A narrow pass separates these two mountain…
Average elevation: 70 m
Make a donation
Laguna
Laguna is home to 24 mountains, most of which are inactive volcanoes. The highest peak in Laguna is Mt. Banahaw, with an elevation of 2,170 m (7,120 ft). Banahaw, unlike most other volcanoes in Laguna, is an active complex stratovolcano, which last erupted in 1843. Banahaw is located in the boundary of Laguna…
Average elevation: 183 m
Tarlac
Like the rest of Central Luzon, the province has three distinct seasons: summer from March to June, monsoon rain from July to early October, and monsoon winter from late October to February. Summer months, especially during May bring frequent, sometimes severe, thunderstorms with high winds, thunder, and hail.…
Average elevation: 217 m
Calbayog
Forty percent of the city's land area are plain and hilly terrains with elevation ranging from 5 to 20 metres (16 to 66 ft) above sea level. The rest are rugged mountain ranges with elevations from 300 to 700 metres (980 to 2,300 ft) above sea level. Flooding is minimized because of many rivers, brooks,…
Average elevation: 78 m
Angeles
Sapangbato is the largest barangay in Angeles in terms of territory, with a total land area of 104,694 sq. meters and a population of 11,262. Located northwest of Angeles near Clark Freeport Zone, it is identified as the barangay in Angeles with the highest elevation of 750 feet above sea level. It is home to…
Average elevation: 98 m
Make a donation
Batangas
Batangas is a combination of plains and mountains, including one of the world's smallest volcanoes, Mt. Taal, with an elevation of 600 metres (2,000 ft), located in the middle of the Taal Lake. Other important peaks are Mount Macolod with an elevation of 830 metres (2,720 ft), Mt. Banoy with 960 metres (3,150…
Average elevation: 126 m
Make a donation
Make a donation
Marikina River
The river's depth ranges from 3 to 21 metres (9.8 to 68.9 ft) and spans from 70 to 120 metres (230 to 390 ft). It has a total area of nearly 75.2 hectares (0.752 km2) and is 27 kilometres (17 mi) long. The riverbank has an elevation of 8 meters above sea level at the boundary of San Mateo and Marikina. This…
Average elevation: 66 m
Make a donation
Antipolo
Its higher elevation than that of Metro Manila affords it a scenic view of the metropolitan area, especially at night. Its locally grown mangoes and cashews are popular among tourists, as well as suman – a local delicacy made out of glutinous rice. The Hinulugang Taktak National Park, which was once a…
Average elevation: 157 m
Make a donation
Cavite
Another theory proposes that the name is a Hispanicized form of kabit, Tagalog for "joined", "connected", or "attached", referring to the peninsula's topographical relation to the mainland. Edmund Roberts, in his 1821 memoir, stated that the "natives" called it Caveit due to the "crooked point of land…
Average elevation: 88 m
Palawan
Palawan's almost 2,000 kilometers (1,200 mi) of irregular coastline is lined with rocky coves and sugar-white sandy beaches. It also harbors a vast stretch of virgin forests that carpet its chain of mountain ranges. The mountain heights average 1,100 meters (3,500 ft) in altitude, with the highest peak rising…
Average elevation: 44 m
Make a donation
Manila
Almost all of Manila sits on top of centuries of prehistoric alluvial deposits built by the waters of the Pasig River and on some land reclaimed from Manila Bay. Manila's land has been altered substantially by human intervention, with considerable land reclamation along the waterfronts since the American…
Average elevation: 6 m
Make a donation
Make a donation
Make a donation
Panay
Panay island is the sixth largest island in the Philippines by area, with a total land area of 12,011 km2 (4,637 sq mi). Mount Madja-as is the highest point in Panay with an elevation of 2,117 metres (6,946 ft) above sea level, located in town of Culasi in the northern province of Antique. Central Panay…
Average elevation: 117 m
Make a donation
Make a donation
Negros Occidental
Negros Occidental has a tropical climate due to the fact that it is situated close to the equator, being located at least nine degrees north of it. The northern section of the province has a tropical rainforest (Köppen: Af) climate, whereas the southern portion has a tropical monsoon (Köppen: Am) climate.…
Average elevation: 126 m
Make a donation
Nueva Ecija
The province is the largest in Central Luzon, covering a total area of 5,751.33 square kilometres (2,220.60 sq mi). Its terrain begins with the southwestern marshes near the Pampanga border. It levels off and then gradually increases in elevation to rolling hills as it approaches the mountains of Sierra Madre…
Average elevation: 275 m
Mindanao
In the eastern portion of the island, from Bilas Point in Surigao del Norte to Cape San Agustin in Davao Oriental, is a range of complex mountains known in their northern portion as the Diwata Mountains. This range is low and rolling in its central portion. A proposed road connecting Bislig on the east coast…
Average elevation: 149 m
Cebu
Coal was first discovered in Cebu about 1837. There were 15 localities over the whole island, on both coasts; some desultory mining had been carried out Naga near Mount Uling, but most serious operations were at Licos and Camansi west of Compostela and Danao. Active work ceased about 1895 with insurrections,…
Average elevation: 91 m
Make a donation
Make a donation
Valenzuela
The highest elevation point is 38 metres (125 ft) above sea level. Having a surface gradient of 0.55% and a gentle slope, hilly landscape is located in the industrial section of the city in Canumay. The average elevation point is 2 metres (6.6 ft) above sea level.
Average elevation: 6 m
Metro Manila
The Coastal Margin or Lowland is a flat and low plain that faces Manila Bay. Located here is Manila, Navotas, parts of Malabon, and the western part and reclaimed areas of Pasay and Parañaque, where the ground elevation ranges from zero meters on Manila Bay to five meters at the west side of the cities of…
Average elevation: 43 m
Make a donation
Quezon City
In order to make Quezon's dream a reality and to mobilize funds for the land purchase, the People's Homesite Corporation (PHC) was created on October 14, 1938, as a subsidiary of NDC, with an initial capital of ₱2 million. Roces was the chairman of the Board of PHC, and they immediately acquired the vast…
Average elevation: 39 m
Malinao
There was no concentration of land holdings by few families, unlike in other areas of the country. Original families in Malinao have their own pieces of land to work on. The land west of the Aklan River, because of its topography, must have escaped the encomienderos and hacienderos in the early part of Spanish…
Average elevation: 89 m
Make a donation
